Boston Consulting: the latest research on the development trend and future mode of supply chain
The following articles are from BCG Boston Consulting and the author is BCG Boston Consulting
This paper expounds the target vision, important measures and key capabilities of the new regional resilient supply chain.
Source / Boston Consulting (ID: bcg_greater_china)
In recent years, trade disputes, geopolitics, repeated epidemics and other problems have occurred frequently. The traditional supply chain built around the "global division of labor and the pursuit of low cost" is no longer suitable for the current era. It is necessary for enterprises to reshape their global supply chain with the goal of "regionalization and toughness".
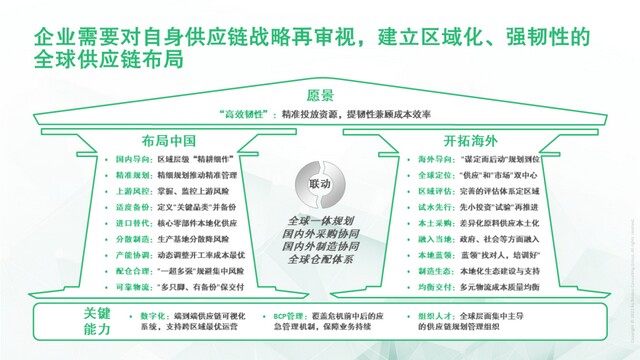
With the trend of double circulation of domestic and foreign economy, most industries will form a new supply chain mode of "integration and double circulation". Focusing on the goal of improving the resilience of the supply chain, enterprises can respectively layout China and expand overseas to create a new supply chain system. However, improving the resilience of the supply chain can not be unilaterally understood as "redundant backup" or "going overseas". Instead, it is to improve the resilience and give consideration to cost efficiency through precise investment of limited resources, which poses a challenge to the supply chain management.
This series of articles describes the objective vision, important measures and key capabilities of the new regional resilient supply chain. The purpose is to help relevant enterprises to layout in advance, rebuild their supply chain and cope with the uncertain future.
01
Challenges: challenges faced by enterprise supply chain under the new situation
In recent years, frequent trade disputes, intensified geographical problems and the epidemic situation have not yet subsided, leading to subversive mode changes and stability challenges in the enterprise supply chain.
Mode change: from globalization to regionalization, China was a "unitary global factory" in the past, and the global supply chain will move towards a "diversified regional market / supply system" in the future.
The upstream risk is intensified: the cost and supply difficulty of the whole chain are significantly increased. The supply problems of key materials such as nickel, lithium and chips occur frequently, and the upstream risk is rapidly amplified.
The concentration of manufacturing area is too high: "egg basket" problem is prominent, the production base layout is single, and it is too far from the consumer market.
The logistics artery has been blocked repeatedly: the delivery channel from products to consumers is blocked, logistics is cost oriented, and warehousing and logistics are not resilient enough to cope with risks.
Faced with the above supply chain challenges, enterprises that actively respond to, rearrange and establish a resilient supply chain can usually achieve significant results.
02
Response: supply chain redistribution, regionalization and strong toughness
To meet the challenges of supply chain, it is necessary for enterprises to deeply understand the current supply chain development trend, establish a systematic supply chain analysis and construction framework, sort out the key measures of supply chain construction, and then reshape their global supply chain.
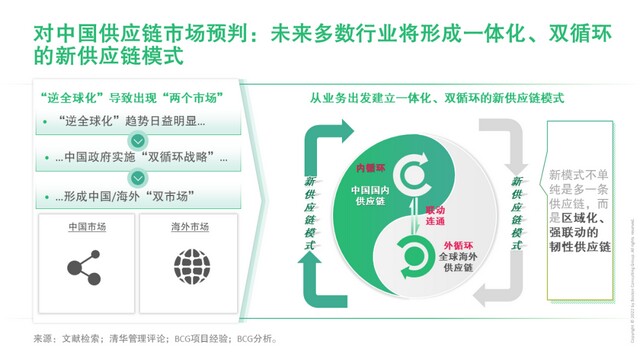
Trend: new supply chain mode of "integration and double circulation"
Framework: vision oriented, domestic and international layout and linkage, key capability support
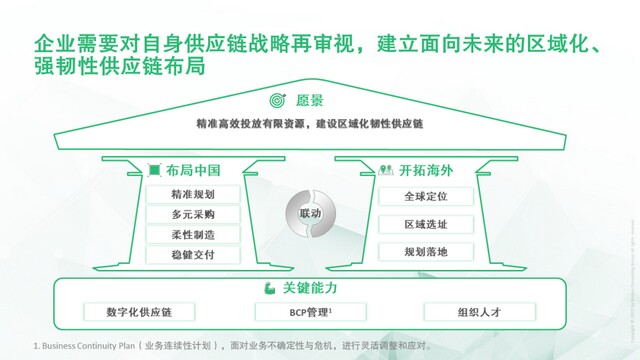
Vision: precise and efficient investment of limited resources to build a regional and resilient supply chain
The trend of "anti globalization" has led to challenges for the global supply chain. In the past, the emphasis on cost and the neglect of resilience need to be strengthened.
However, improving the resilience of the supply chain can not be unilaterally understood as "redundant backup" or "going overseas". Instead, it is necessary to accurately assess the degree of necessity and priority, and use resources to avoid "excessive redundancy and waste". So as to realize the precise investment of limited resources and improve the toughness while taking into account the cost efficiency.
At the same time, for each link of the supply chain, the layout of China needs to be fully linked with overseas development, so as to form a "joint force" at home and abroad, reduce resource consumption, achieve "global optimization" and improve resilience.
Based on this, we refined the key principles of building a regional resilient supply chain:

03
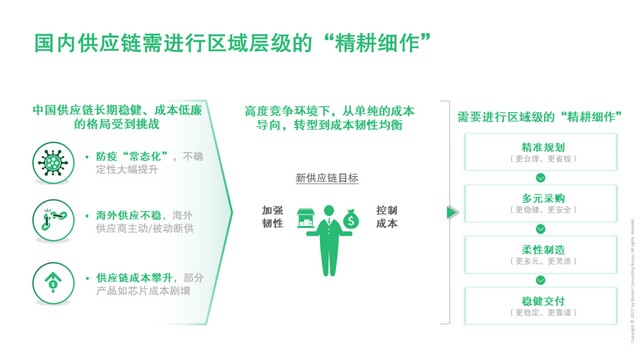
Layout in China: the domestic supply chain needs to carry out "intensive cultivation" at the regional level
Faced with the "normalization" of epidemic prevention, unstable overseas supply and rising supply chain costs, China's long-term stable and low-cost supply chain has been challenged. Under the highly competitive environment, China's supply chain needs to transform from a simple cost oriented to a cost resilient equilibrium. It is necessary to carry out "intensive cultivation" at the regional level to achieve accurate planning, diversified procurement, flexible manufacturing and stable delivery.
Accurate planning: the planning granularity is refined to improve the prediction accuracy and support the accurate allocation of supply chain resources. The whole planning process is refined from the national level to the regional level, so as to improve the accuracy of resource allocation and avoid "blindly adding redundancy", so that when dealing with emergencies such as epidemic prevention and isolation, each region can "become one". Improve the accuracy of regional prediction and ensure that the regional prediction results are more accurate and can be used to support regional level planning.
Diversified procurement: identify upstream risks, conduct key backup and localized procurement.
1) Upstream risk: clearly map the upstream in-depth supply chain, comprehensively grasp the upstream situation, and effectively monitor and respond to risks. For example, a leading aircraft manufacturing enterprise combs the information of tier 2 and Tier 3 suppliers, analyzes their operations, and monitors potential risks in real time to solve them.
2) Key backup: identify the scarcity and impact of raw materials, identify "bottleneck items" with high strategic importance and high procurement risk (few suppliers), and make appropriate backup of suppliers / materials. For example, a leading global automobile company changed the principle of "just in time production and reduce backup" (JIT) after the outbreak of the epidemic, and reserved chips for backup for 2-6 months. After the chip crisis, it still maintained full production and its sales volume exceeded that of its competitors.
3) Localized procurement: at present, the risk of active / passive supply interruption of overseas suppliers is high. Chinese enterprises can realize localized procurement by supporting local suppliers and investing in the upstream of the industrial chain. For example, a domestic leading new energy automobile enterprise has built an upstream chip industry chain, with stable supply chain chips and rapid sales growth.
Flexible manufacturing: diversified production bases are conducive to reducing risks, flexible capacity allocation and optimal cost.
1) The diversification of production bases can avoid the potential risks caused by the centralized layout of a single region: consider the market, category, raw materials, etc. for decentralized layout, from a centralized large base to a decentralized small base. For example, a new energy vehicle enterprise has diversified production capacity layout, and its factories are scattered in 8 provinces and cities. With reasonable production capacity distribution, the containment of the epidemic in a single city will not lead to a major crisis.
2) Dynamic capacity allocation is carried out in multiple production bases to meet the needs of customers. The cost is optimal: the supply and demand, raw materials, manufacturing, logistics and other factors of each production base change frequently, resulting in the fluctuation of unit production cost. The operating rate is adjusted in real time based on the cost change to achieve the lowest total cost. For example, in a leading international beer enterprise, the system conducts analysis and Simulation on the basis of production cost, predicted sales volume, inventory, and the impact of out of stock every month, and recommends the optimal combination of factory operating rates to dynamically adjust the operating rates of 26 domestic factories.
Stable delivery: the warehouse network layout is reasonable, and the delivery logistics is backed up.
1) The layout and configuration of the warehouse system are reasonable, and the functions of the core warehouse are strengthened: to avoid one warehouse spreading to the whole country, and to avoid warehouses everywhere, so as to balance the costs and risks of the warehouse; The warehouse is managed by level, with the layout of "one super multi strong". One national distribution center (NDC) manages multiple regional distribution centers (RDC), focusing on strengthening the NDC function. For example, a leading beer enterprise originally had only one warehouse in Wuhan. In the past 20 years, Wuhan suffered heavy losses due to the epidemic. Subsequently, four warehouses were built throughout the country for decentralized distribution; A leading sportswear enterprise has set up one NDC and four RDCs throughout the country to focus on strengthening the NDC capacity, and NDC can make offline and online goods at the same time.
2) The delivery logistics "has multiple legs and backup" to improve the reliability of logistics delivery: introduce diversified logistics service providers to deal with emergencies, reduce costs by economic logistics at ordinary times, and ensure delivery by quality logistics at critical times of the epidemic. For example, a leading beer enterprise originally entrusted a small regional logistics company to reduce costs; After the epidemic, the industry-leading logistics service provider was introduced to ensure access during the epidemic.
04
Summary of enterprise building regional flexible supply chain
To sum up, the current situation promotes the enterprise supply chain to shift from "globalization and low cost" to "regionalization and strong toughness". Faced with changes, enterprises need to:
Define the vision of "high efficiency and toughness" and reach a consensus within the enterprise;
The "regional level" of the domestic supply chain is carefully planned to improve resilience but avoid high costs.
The planning is implemented from the global to the regional level, and resources are allocated accurately to avoid infinite redundancy;
Monitor the upstream risk of procurement, and conduct key backup and localized procurement;
Diversified production bases disperse risks, and the cost of dynamic capacity allocation is optimal;
The warehouse and delivery logistics have "backup" to realize stable and reliable delivery.
05
Overseas supply chain construction
When developing overseas supply chain, enterprises will enter a new environment and face greater uncertainty. The risk is much higher than that at home. Therefore, it is necessary to make a good plan first, balance resilience and resources, and implement the plan after it is in place.
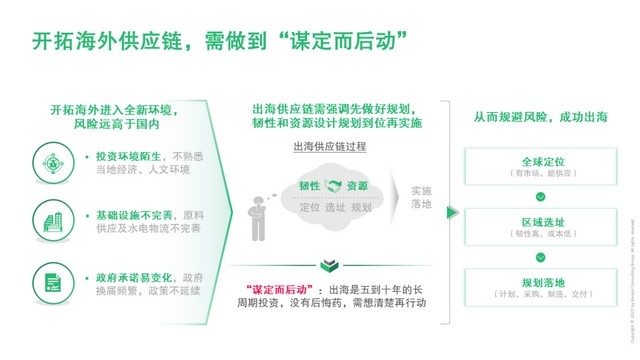
1. Global positioning
The strategy of "selling real estate" (deploying production in the target sales market) can use the market to balance supply chain risks and improve resilience. "Supply convenience" and "regional market" shall be considered simultaneously in the site selection and layout. The supply chain shall be close to the market and the market shall be used to balance the supply chain risks. For example, a state-owned enterprise invested in a cotton textile factory in Tanzania, Africa, to avoid the tariff imposed by the United States, and only positioned itself as a supply center. Subsequent tariff changes led to the loss of cost advantages, the lack of local market and the inability to digest local production capacity, and finally, it was at a loss; An electronic OEM enterprise develops the Indian market, takes into account the supply chain and the local market, and has a large number of local orders, which can hedge the strike, default and other risks of the local supply chain in India.
2. Regional site selection
Establish a sound evaluation system, fully consider the medium and long-term risks of five to ten years, and select the investment area. Before investment, it is necessary to carefully consider the risks, consider various scenarios, and make plans for the risks before making decisions.
We will refuse to blindly invest overseas. We will first "test" small-scale investment and then promote it after confirmation. For example, an electronic technology enterprise first tried to invest in Czech Republic, Brazil, Vietnam and other countries. After verification and comparison, Vietnam has obvious advantages, and subsequently decided to invest in Vietnam on a large scale.
3. Planning landing
Plan: plan based on the local market. It is necessary to establish an independent localization planning team to deeply understand the logic behind the operation of the local market, so as to formulate a planning plan that meets the local needs.
Procurement: guarantee the supply of differentiated raw materials. After going to sea, the supply chain is in front, and the general raw materials can be transported from China. However, the transportation of differentiated raw materials is difficult to guarantee quality and quantity, so it becomes a "bottleneck", and the supply needs to be localized. For example, in the Vietnam factory of a garment OEM enterprise, general-purpose chemical fibers are imported from China, while differentiated fabrics are provided by establishing independent factories in Vietnam to avoid supply chain risks.
Manufacturing: promote the localization of manufacturing. After the localization of manufacturing, the dependence on the local market has greatly increased, and the domestic assistance has decreased. Therefore, we must make good use of local resources.
1) Integrating into the local society: including establishing good interaction with the government, influencing government policies, improving the social image of the enterprise in the local area, and appointing influential people in the local area as senior executives;
2) Make good use of local blue collar: the blue collar focuses on recruiting hard-working local employees, and strengthens training to master core skills; Dispatch key talents who understand the company's needs and culture and can manage local employees well to go to sea;
3) Develop local ecology: cooperate with local digital enterprises to develop tools, develop and empower local equipment maintainers to ensure equipment operation, mobilize domestic resources and improve local professional service quality.
Delivery: adopt multiple logistics Collocations to balance delivery quality and cost. Overseas and local logistics are faced with difficulties, and suitable logistics service enterprises can be selected in combination with product importance and timeliness requirements to form a combination of international logistics, local leading logistics and ordinary logistics, so as to achieve cost and timeliness balance.
4. Key ability training
To build a regional and resilient supply chain, it is also necessary to improve the key capabilities such as digital visualization of supply chain, business continuity planning (BCP) and global planning and management.

Digital capability: digital intelligence enables the supply chain to be globally open and interconnected to realize the optimal operation of the cross regional supply chain. By establishing an end-to-end supply chain visualization system, support management optimization and improve supply chain efficiency.
BCP Management: establish and improve the crisis response mechanism, be prepared, adjust and summarize. We should have rules and regulations to deal with crises, make optimal decisions, fully mobilize resources and strengthen resilience, so as to ensure the smooth operation of business.
Organize talents: establish a supply chain planning and management organization led by the global level, and clarify the responsibilities of relevant personnel in each process to ensure that the supply chain can cooperate at the global level and achieve the optimal solution.
06
Summary of enterprise building regional flexible supply chain
To sum up, the current situation promotes the enterprise supply chain to shift from "globalization and low cost" to "regionalization and strong toughness". Faced with changes, enterprises need to:
Define the vision of "high efficiency and toughness" and reach a consensus within the enterprise.
The domestic supply chain is carefully planned to improve resilience but avoid high costs.
The offshore supply chain "plans before moves", balances resilience and resource input, and reduces investment risks.
Lay a solid foundation, including key capabilities such as digitization, emergency management and organization of talents.
Source / Boston Consulting (ID: bcg_greater_china)
About the author
Chen Qinglin is the managing director and global partner of Boston Consulting Group (BCG) and the head of BCG logistics, transportation and supply chain business in China.
Wei Jincheng is the managing director and global partner of Boston Consulting Group (BCG) and the core leader of BCG logistics, transportation and supply chain business in China.
Peng Yong is the managing director of Boston Consulting Group (BCG) and a core member of BCG's logistics, transportation and supply chain business in China.
Duan Ye is the managing director of Boston Consulting Group (BCG) and a core member of BCG's logistics, transportation and supply chain business in China.
Thank BCG colleagues Xu Qian, Zhao Wenqi, Li Quanjia, Chen Lifeng, Guo Dongsheng and Chen Jiayi.


